One of the big questions in digital marketing right now (and it’s only going to get bigger) is… What are people asking ChatGPT about/for?
Data has been thin on its feet in this department since the platform’s release and meteoric rise immediately thereafter. But, over time, fragments of information have been surfacing, recently culminating in an extensive study by none other than OpenAI themselves.
In this post, we explore the hard data directly tied to ChatGPT usage, as well as complementary research and supporting signals that let us make educated inferences about how people are using the platform and the kinds of queries they’re typing in.
TL;DR – How people are really using ChatGPT
- Around 70% of ChatGPT use is non-work related, with most queries focused on everyday guidance, information, and writing.
- For work tasks (30% of use), the biggest activities are documenting information, problem-solving, creative thinking, and technical support.
- ChatGPT interactions fall into three broad “modes”: Asking, Doing, and Expressing — a useful lens for understanding user intent.
- Asking is the most common intent, showing that ChatGPT is now primarily used as a search engine.
- By looking at ChatGPT’s most-cited sources (e.g. Reddit, Wikipedia, Amazon, Forbes), we can infer six “big buckets” of global use: advice, education, shopping, news, business, and entertainment.
- Assuming people use ChatGPT in areas they believe AI is good at, common UK uses may include simple maths, complex maths, general knowledge inquiries, proof reading, drafting emails, and summarising complex topics.
Why read on?
The sections below provide detailed context on work vs. non-work use, user intent, and common query types. Brands, content creators, and educators can use these insights to better align content, tools, and guidance with the situations in which people actually turn to ChatGPT.
Find out what still matters for effective SEO in 2025.
The big picture – how ChatGPT is being used overall
ChatGPT usage is incredibly varied across different demographics and contexts, but the most common tasks people bring to ChatGPT are:
- General research
- Academic research
- Coding assistance
- Email composition
- Marketing copy
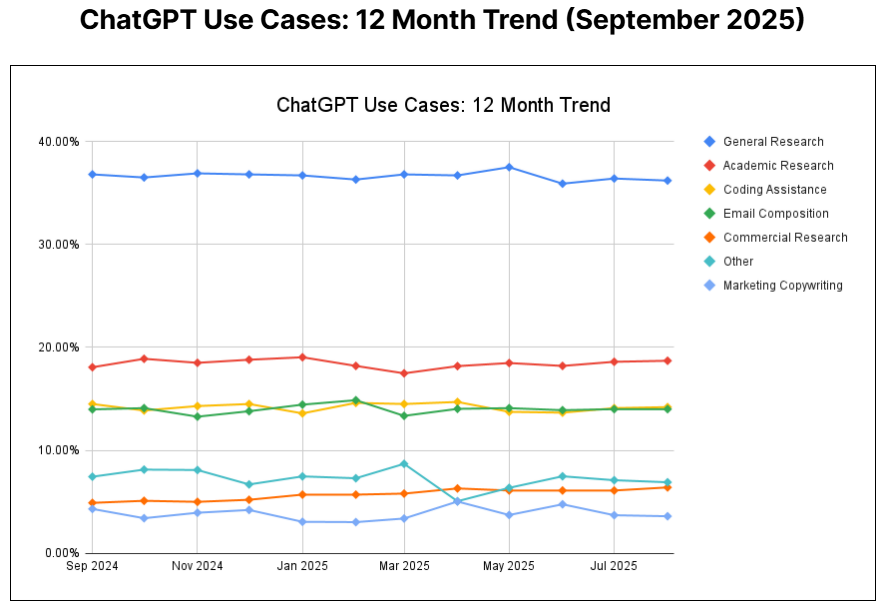
Source: Firstpageseo
Looking at these use cases alone, you’d be forgiven for thinking that ChatGPT is used primarily in professional contexts, but research from OpenAI proves otherwise.
ChatGPT use data from OpenAI research
OpenAI’s economic research team collaborated with Harvard economist David Deming to carry out the largest study to date on how people are actually using ChatGPT.
The goal of the study was to assess the economic impact and value of ChatGPT, but it’s also a treasure trove of insights for marketers hoping to build presence and reach certain audiences on and through ChatGPT.
Get comprehensive digital marketing support from TDMP.
Analysing 1.5 million actual messages between ChatGPT and its users, the research supergroup discovered the vast majority of usage centres on completing everyday tasks. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg!
ChatGPT modes of interaction explained
Roughly three-quarters of conversations monitored during the study fell into practical categories (seeking guidance, looking up information, or drafting content).
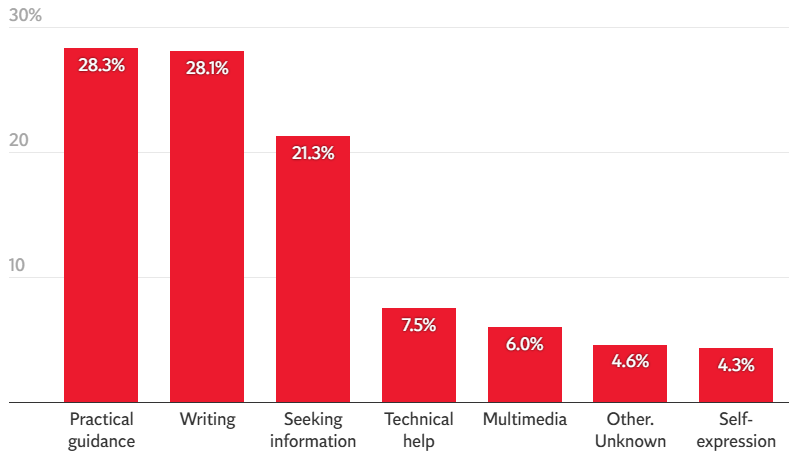
Source: Independent
These patterns can be grouped into three modes of interaction: Asking, Doing, and Expressing.
- Asking (49%): Nearly half of messages are requests for advice, explanations, or insights, highlighting that people increasingly turn to ChatGPT as an advisor rather than just a tool for execution. These are the tasks that would normally be reserved for traditional search engines.
- Doing (40%): Task-oriented interactions such as drafting, planning, and coding, which also account for about a third of work-related use.
- Expressing (11%): A smaller but distinct share, where people use ChatGPT for reflection, creativity, or play.
These “modes” can be thought of as the high-level user intent behind any ChatGPT interaction. They can inform how businesses position themselves to be discoverable in AI-driven conversations because knowing whether users are seeking advice, execution, or expression shapes the kind of content and answers they’re most likely to encounter.
Work vs non-work ChatGPT usage
One of the most interesting aspects of OpenAI’s study is that it clearly distinguishes between work- and non-work-related interactions, giving us detailed usage insights specific to the professional and private realms.
The study concluded that only about 30% of ChatGPT usage is work-related, with the 70% majority pertaining to non-work activities.
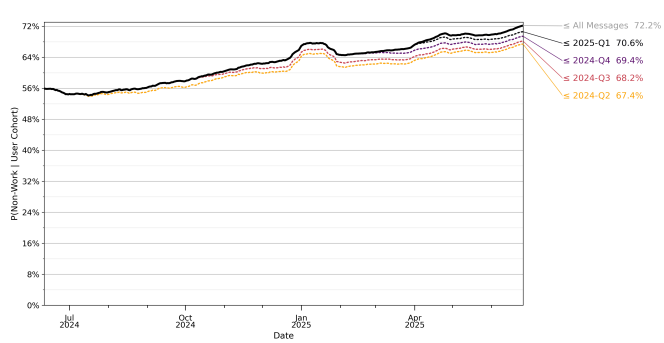
Source: OpenAI/National Bureau of Economic Research
The solid black line in the above table shows the probability that a message on a given day is not work-related. Conversation topics for these non-work interactions most often focused on practical guidance, followed closely by information seeking, and writing:
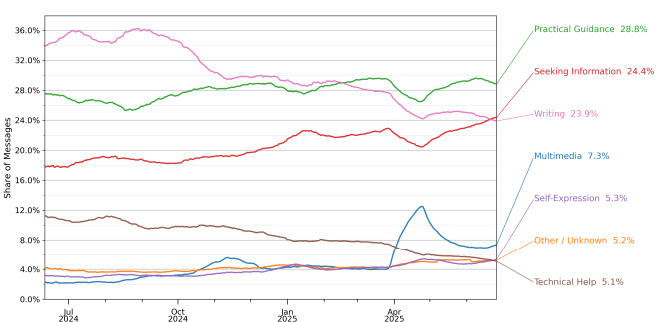
Source: OpenAI/National Bureau of Economic Research
For messages that were related to work, the same three topics were observed, albeit in a different order: writing tasks were significantly more common than practical guidance, which came in second, and seeking information, which placed third.
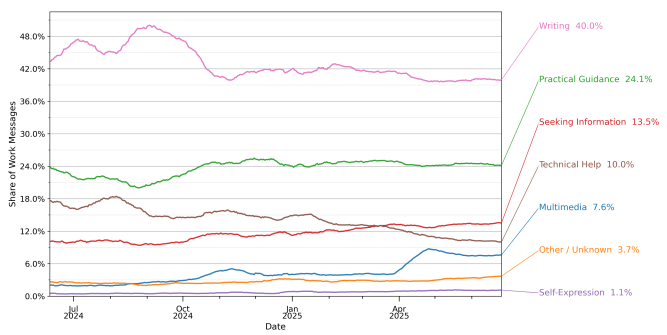
Source: OpenAI/National Bureau of Economic Research
As most ChatGPT use happens outside of work, to connect with users, content should meet them where they seek guidance, information, or inspiration in everyday contexts, not just professional tasks.
That said, whether for work or personal use, people most often turn to ChatGPT for writing, guidance, or information, meaning content geared towards these categories may boost visibility across both audience types.
Explore SEO services for building visibility in traditional and AI search.
Work vs non-work ChatGPT message intents
The work/non-work fingerprint of observed messages can be grouped by general user intent, giving us an understanding of the differences in why people turn to ChatGPT inside versus outside of work.
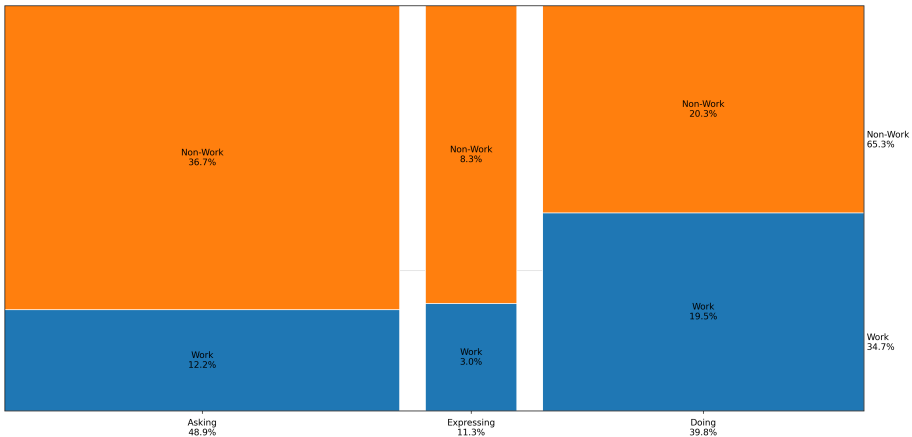
As shown in the table above, due to non-work-related queries accounting for significantly more of the total messages than work-related queries, they form the majority for each intent.
Chief among these majorities is the “Asking” intent, followed by “Expressing”, and finally “Doing”. For work-related queries, the inverse is true, with “Doing” being the most common intent, and “Asking” being the least common.
Top work-related activities with ChatGPT
OpenAI’s research categorises people who use ChatGPT for work purposes into the following broad professional categories:
- Computer-related
- Engineering
- Management & business
- Other professional
The study revealed that the topic of work-related messages to ChatGPT differ dramatically based on these groupings:
- Writing-related messages are most common among users in management/business roles, and least common in computer-based roles.
- Technical help-related messages are, conversely, most common among users in computer-based roles, and least common in management/business roles.
- Information seeking messages are most common across users in engineering professions, while users in computer-based roles are least likely to enter purely informational queries.
- Practical guidance-related messages are most common outside the main categories, and least common among management/business users.
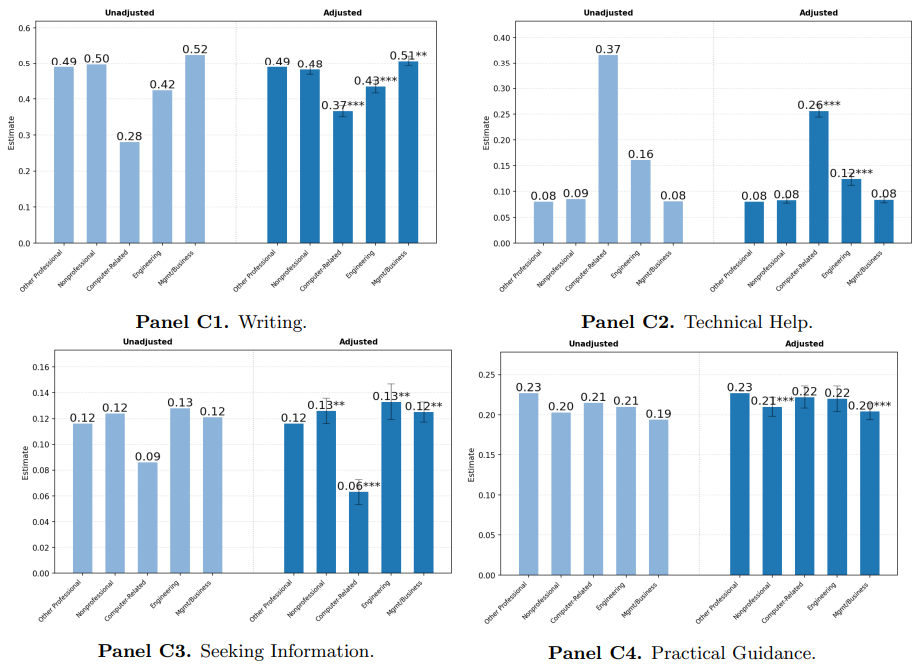
Source: OpenAI/National Bureau of Economic Research
The study then digs deeper, organising all analysed work-related ChatGPT messages into more specific work activities (Generalised Work Activities - or GWA), researchers found that just 7 of the 37 GWA categories accounted for 81% of all use:
- Documenting/recording information - (18.4%)
- Making decisions & problem-solving - (14.9%)
- Thinking creatively - (13%)
- Working with computers - (10.8%)
- Interpreting the meaning of information for others - (10.1%)
- Getting information - (9.3%)
- Providing consultation & advice to others - (4.4%)
Individually accounting for between 1 and 3% of work-related messages, the following 5 ChatGPT work activities are also notable:
- Analysing data or information - (3%)
- Communicating with supervisors, peers, or subordinates - (2.8%)
- Judging the qualities of objects, services, or people - (2%)
- Communicating with people outside the organisation - (1.4%)
- Estimating the quantifiable characteristics of products, events, or information - (1%)
Detailed work-related ChatGPT task breakdowns
The report also offers a more granular analysis of work-related conversation topics across some of the top-level categories, including:
- Writing -
- Editing or critiquing existing text (10.6%)
- Personal writing or communications (8%)
- Translation (4.5%)
- Argument or summary generation (3.6%)
- Writing fiction (1.4%)
- Practical guidance -
- Tutoring or teaching (10.2%)
- “How to” advice (8.5%)
- Health, fitness, beauty, or self-care (5.7%)
- Creative ideation (3.9%)
- Information seeking -
- Specific information (18.3%)
- Purchasable products (2.1%)
- Cooking and recipes (0.9%)
- Multimedia -
- Image generation (4.2%)
- Generating or retrieving other media (1.1%)
- Analysing an image (0.6%)
- Technical help -
- Computer programming (4.2%)
- Maths calculations (3%)
- Data analysis (0.4%)
- Self-expression -
- Greetings and chitchat (2%)
- Relationships & personal reflection (1.9%)
- Games and role play (0.4%)
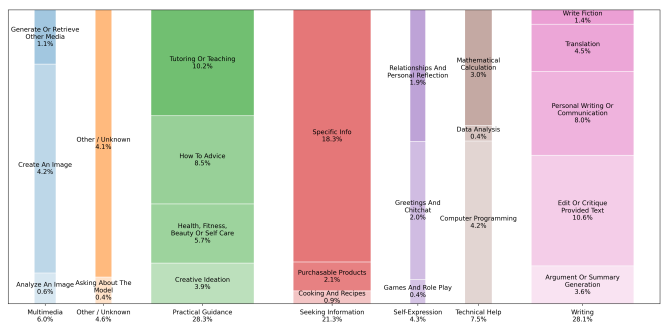
Source: OpenAI/National Bureau of Economic Research
Brands may be able to boost visibility in ChatGPT outputs by creating clear, actionable content in these areas, especially tutorials, advice, and high-quality informational resources.
Educational applications of ChatGPT – Insights from social media
An ingenious study analysed social media to gather data on ChatGPT use direct from the social posts of the platform’s users.
Focusing on educational applications, the researchers carried out social media content analysis (SMCA) across Reddit, Twitter, YouTube and LinkedIn, essentially scraping the platforms for posts discussing first-hand ChatGPT use.
We have reviewed the paper and condensed the main findings into the below infographic:
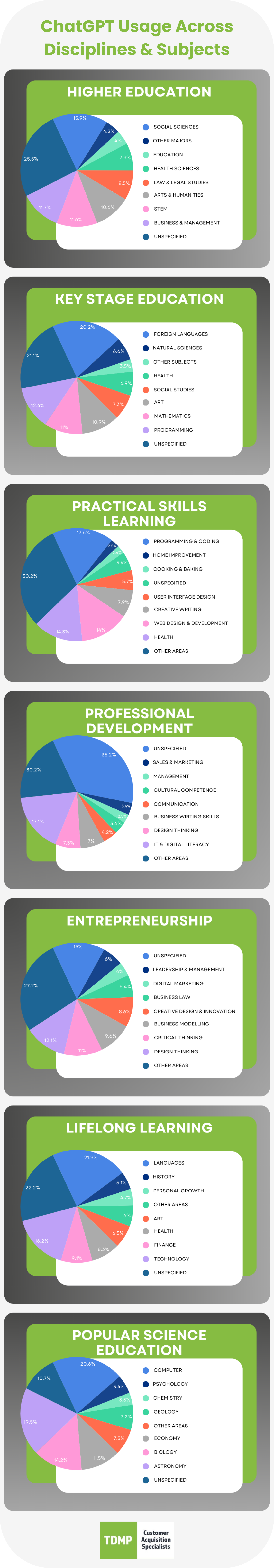
Looking at the data, some clear themes emerge. Across educational levels, STEM, business and management, and programming/coding stand out as the most common subjects where people use ChatGPT. That tells us where audiences are actively seeking information, guidance, and inspiration — and where brands have the best chance to meet them:
-
STEM & technology: Publish explainers, case studies, or interactive tools that make complex topics accessible to learners and professionals.
-
Business & management: Share insights around leadership, strategy, and digital transformation — areas where users already turn to AI for insights.
-
Programming & coding: Offer tutorials, AI-driven learning experiences, or developer-focused content that supports self-learners and upskillers.
Reverse engineering ChatGPT query topics from top-cited sources
There may not always be granular data on the word-for-word queries people are typing into ChatGPT (yet), but we do know ChatGPT’s most cited sources. Starting from here, we can work backwards with logical assumptions to infer details about ChatGPT use.
1. Reddit
- Why it’s cited: Reddit often has first-hand experiences, niche communities, and practical advice.
- Potential user query areas:
- “What’s the best laptop for students in 2025?”
- “How do I negotiate a salary increase?”
- “Personal experiences with ADHD / weight loss / gaming PCs / crypto.”
- Theme: Everyday life advice, product comparisons, lived experiences, social commentary.
2–5. Wikipedia (en, es, de, fr)
- Why it’s cited: For factual background, definitions, summaries across languages.
- Potential user query areas:
- “Explain quantum computing in simple terms.”
- “Who was Marie Curie?”
- “What’s the history of Israel’s occupation of Palestine?”
- Theme: General knowledge, history, science, global current events.
6. Amazon
- Why it’s cited: Product listings, specs, and user reviews.
- Potential user query areas:
- “Best budget wireless headphones under $100.”
- “Top-rated kitchen gadgets in 2025.”
- “Compare Kindle models.”
- Theme: Shopping, product comparisons, consumer tech, lifestyle products.
7. TechRadar
- Why it’s cited: Consumer technology news, buying guides, reviews.
- Potential user query areas:
- “Which iPhone should I buy in 2025?”
- “Best VPNs right now.”
- “Upcoming gaming laptops.”
- Theme: Consumer electronics, cybersecurity, software tools, tech trends.
8. The Sun
- Why it’s cited: Pop culture, trending stories, celebrity news.
- Potential user query areas:
- “Who is dating [celebrity]?”
- “Latest on the Premier League.”
- “Reality TV news.”
- Theme: Entertainment, celebrity gossip, sports news, viral trends.
9. Times of India
- Why it’s cited: Global and Indian news, current events - ChatGPT is big in India.
- Potential user query areas:
- “Latest news about India’s elections.”
- “What’s happening with India’s economy?”
- “Bollywood news updates.”
- Theme: Politics, economics, local/global news, Bollywood, cricket.
10. Forbes
- Why it’s cited: Business, finance, entrepreneurship, rankings.
- Potential user query areas:
- “Top startups in AI right now.”
- “Richest people in the world 2025.”
- “Investment strategies during inflation.”
- Theme: Business trends, wealth, entrepreneurship, finance, workplace culture.
The “big buckets” of ChatGPT use (based on top citations)
From ChatGPT’s top cited sources, we can infer the main themes of ChatGPT usage globally:
- Everyday life & personal advice: Reddit
- General knowledge & education: Wikipedia (multiple languages)
- Shopping & consumer products: Amazon, TechRadar
- News & current events: Times of India, The Sun
- Business & finance: Forbes
- Entertainment & sports: The Sun, Times of India, Reddit
Estimating ChatGPT applications based on perceived AI abilities
A recent YouGov poll asked UK respondents what they felt AI chatbots like ChatGPT are good at, rating them on a scale from very bad to very good across a number of different applications.
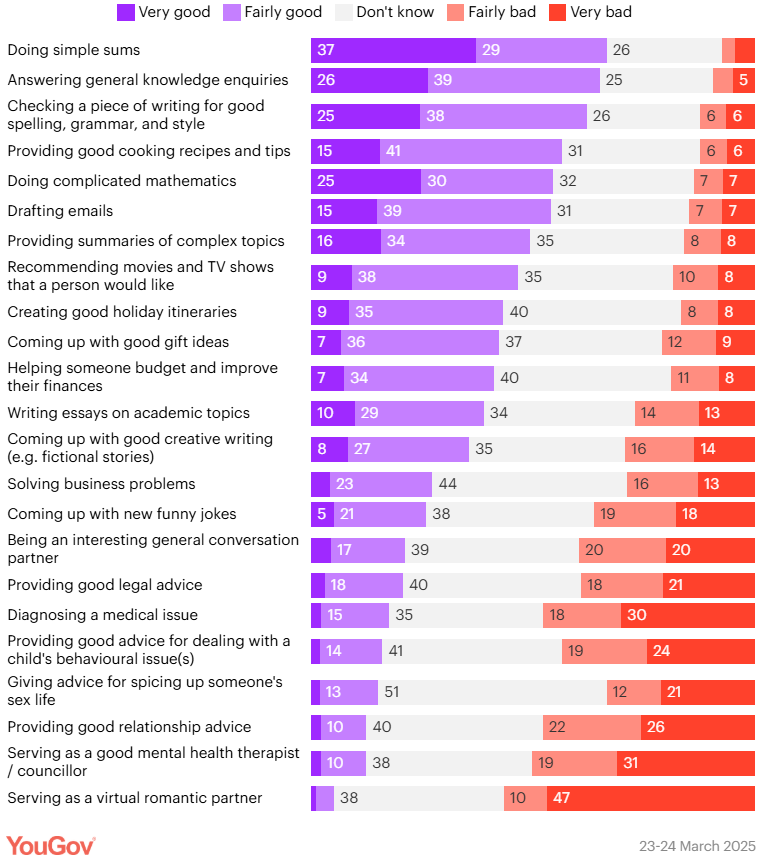
Source: YouGov
While this data doesn’t directly reveal how people use ChatGPT (or other AI search tools), it’s reasonable to assume they turn to it for tasks they believe it can handle well. With that in mind, the table above offers useful clues about the kinds of tasks and questions people are likely taking to ChatGPT — as well as the ones they may not.
Looking at the tasks people see AI as “good at”, it’s easy to see why certain businesses would benefit from being visible in ChatGPT outputs…
A recipe platform or food brand gains value if ChatGPT suggests their cooking tips. Travel companies benefit when users ask for holiday itineraries. Streaming platforms, book publishers, or lifestyle blogs stand to gain if their recommendations shape what people watch or read. Even financial services providers have a stake, since people turn to ChatGPT for budgeting help and advice on managing money.
Key Takeaways – What does use case data tell brands about building a presence in ChatGPT conversations
Based on usage patterns and content trends, brands may be able to strategically increase their presence in ChatGPT outputs by focusing on the following:
- Creating actionable guidance: Tutorials, “how-to” content, and practical tips can perform well because users frequently turn to ChatGPT for advice, problem-solving, and everyday guidance.
- Offering high-quality informational content: Clear, authoritative answers to specific questions (product comparisons, educational explanations, or technical advice) may boost visibility, as information-seeking is a major interaction type.
- Consider technical niches: While smaller in volume, requests for images, coding help, and calculations indicate opportunities for brands in tech, design, or STEM-related spaces.
- Thinking beyond work use: Most interactions are non-work-related, so content that appeals to everyday interests (food, fitness, personal finance, lifestyle tips, entertainment) can reach a broader audience.
- Leveraging top-cited sources for inspiration and value-checking: Although ChatGPT’s favourite sources show what sort of content is in demand, for certain query types, ChatGPT will almost always rely on these major authorities. When creating content, brands should assess whether their topic falls into this “top-source” category. If it does, adding unique expertise, fresh insights, or practical examples can increase the chances of being cited, rather than being overshadowed by the big names.
Build your digital presence with TDMP
ChatGPT is rapidly becoming a key channel for information, guidance, and inspiration, both for work and everyday life.
Brands that understand how users interact with the platform, the content types ChatGPT leans on, and the areas where unique expertise can stand out are better positioned to increase visibility and influence AI-driven conversations.
For support building visibility in traditional and AI-powered search results, contact TDMP to develop a strategy that puts your content in front of the right audiences.

