We didn’t exactly need a crystal ball to see fully search-integrated Gemini in Google’s future. But in late 2024, we got the first bit of hard evidence that the tech giants are actively working on the project.
Just another Google feature? Not exactly. Imagine AI Overviews were served without the traditional blue link listings, and only webpages cited by the overview gain clicks from searches. That’s the search format that ‘AI Mode’ presents — and wide take-up could have a drastic impact on your web traffic.
In this post, we cover everything we currently know about Google AI Mode, including capabilities, appearance, and projected impact.
Updates (28/07/25)
- Google places AI Mode button in main search bar for US users
US users can now access AI Mode directly in the main Google search bar - on the search landing page.
Source: Search Engine Roundtable
As covered in this post earlier in the year, AI Mode was initially only accessible via the filter tabs that sit beneath the search bar on a SERP. This change means AI Mode is immediately available to searchers, further reducing exposure to Google's traditional SERPs, highlighting the importance of visibility in AI Mode's output. Contact TDMP to talk AI strategy.
- Google launches paid upgrades for AI Mode
AI Mode is now running on Google's latest AI model, Gemini 2.4 Pro - but only for Google AI Pro and AI Ultra subscribers.
According to Google, Gemini 2.5 Pro, 'excels at advanced reasoning, math and coding questions, helping you with your complex queries with links to learn more.'
Google have also launched Deep Search in AI Mode, again, for paying subscribers only.
Deep Search is a research-oriented facet of AI Mode that can 'save hours by issuing hundreds of searches, reasoning across disparate pieces of information and crafting a comprehensive, fully-cited report in minutes.'
These new AI Mode features will likely be made available to all users in the not-too-distant future.
What is AI Mode for Google Search?
AI Mode is Google’s evolving answer to ChatGPT-style search. Instead of a traditional list of blue links, AI Mode lets users engage in conversational exploration with generated responses. It’s powered by a customised Gemini 2.0 model, designed to handle highly complex queries, understand context, and support follow-up questions.
The feature builds on Google’s earlier experiments like Search Generative Experience (SGE) and AI Overviews. While AI Overviews overlay generated summaries above classic search results, AI Mode replaces the SERP entirely with a chat interface—though it can still show links to sources.
Multimodal capabilities are central to AI Mode. Users can search via text, voice, or images (through Google Lens). For example, you can upload a photo of a product and ask for comparisons, or use voice input to query conversationally.
Why publishers should be concerned about Google's AI Mode
We may be in the middle of an AI boom, but beyond professional contexts, AI is yet to really take centre stage and become normalised among the general public — Google AI search could do just that.
ChatGPT and similar tools are already enticing people to drop traditional search for a more flexible and conversational alternative, removing classic SERPs (and all the clicks they broker) from the equation.
But considering Google’s vast user base, broad implementation of full Gemini search would set this migration into hyperdrive. We could see a sizeable and sudden influx of users making the switch, drastically impacting website performance as SERPs are left behind.
How is AI Mode impacting your performance metrics?
AI Mode will accelerate the impacts of AI Overviews we've been observing throughout its first year of activity. Namely:
- Reduced organic traffic - AI Mode aims to give users what they need without clicking through to websites and reading original content.
- Keyword ranking is meaningless - As AI Mode uses a sophisticated semantic approach to determine search intent (something Google has been using and building on for years), keyword ranking doesn't apply, making it impossible to track.
What material impact does this have on website performance?
Clicks may be in decline — but, importantly, it's primarily low quality clicks that are intercepted by AI Mode. These are generally the people who have low-depth informational queries and are not looking to engage meaningfully with your content or seriously consider your offerings.
On the other hand, users looking for services will not be satisfied with AI Mode's informational response and will actively seek websites of businesses who can meet their needs.
As long as you're visible within AI Mode (as a cited source or recommended entity), the clicks you do receive tend to be of a much higher quality and far more likely to convert.
How and where is AI Mode rolling out?
AI Mode first appeared in 2024 code references but went public in March 2025 as a Search Labs experiment for Google One AI Premium subscribers.
Since then, its rollout has accelerated:
- March–April 2025: Early testing in the US for Premium users
- June 12, 2025: Full public launch across the United States
- June–July 2025: Initial limited release in India through Search Labs
- Two Weeks Later: Full release to all Google users in India
- Expected Next: Google typically prioritises the UK (or occasionally Japan/Brazil) for major launches, suggesting UK availability is imminent, likely after a brief testing window
Additionally, AI Mode is now available to Workspace accounts in the US, including integrations with circle-to-search and Lens searches—though these trigger only if the query qualifies for an AI Overview. Users can scroll to the bottom of an overview and tap “Dive deeper with AI Mode” to continue exploring.
Capabilities and user experience
AI Mode allows:
- Rich conversational answers with the option to ask follow-up questions
- Voice and image-based search inputs
- Dynamic retrieval of citations (results can differ with each refresh)
- Highlighting of quoted text on source pages to improve transparency
The dynamic retrieval is particularly notable. US users have observed that refreshing the same query often yields different cited sources. This suggests AI Mode draws on a wider swath of Google’s index and can surface references beyond the first SERP, giving lower-ranked sites more opportunities for visibility.
Even so, traditional SEO remains vital. AI Overviews are increasingly overlapping with the first page of Google, and the systems underlying AI Mode still draw on the same index, ranking signals, and quality indicators. A strong organic ranking improves your odds of inclusion across all these surfaces.
Insights from beta testing and early use
Early testers uncovered several patterns and quirks in how AI Mode performs:
- Local Context by Default: Many outputs included locational information even when the query didn’t imply it. Whether this is by design or something Google will temper once the beta use data starts rolling in is unclear.
- Bypassing Certain Sites: Searches for high-trust platforms (e.g., Wikipedia, Reddit, CNN, DuckDuckGo) often bypass AI Mode and revert to classic results.
- Long Outputs for Commercial Queries: Responses to product or informational searches can exceed 500 words and contain dozens of citations.
- Greater Visibility for Page 2 Results: When AI Mode is bypassed, the fallback SERPs frequently surface URLs that typically live beyond page 1.
- Small but Important Thumbnails: Cited URLs often include 82x82 px thumbnails, with missing images linked to lower click-through.
- Brand Dominance: BestBuy and other large US retailers appear prominently in commerce-focused results.
- More In-Output Than Sidebar Citations: Some responses include over 20 embedded links but just a few side-panel citations.
- Highlighted Source Text: Clicking a citation often takes users to a page where the quoted passage is highlighted. This is both handy for users and helpful for SEO, as these highlighted sections can be analysed to shine a light on what Google is looking for in a citable passage.
- Fewer Citations on Mobile: Mobile outputs usually show about half the citations of desktop.
- Sparse Citations for Informational Queries: Simple informational searches may produce as few as four citations.
- Blue Links Instead of Traditional SERP Features: For example, this report shows that online travel agencies have seen improved visibility because AI Mode sometimes omits the Google Flights widget.
- Historical Authority Matters: Established sites are more likely to be cited.
- Real-Time and Locational Emphasis: The AI search market is becoming increasingly saturated. Google is hoping that their access to real-time and locational information helps their product stand out in the crowd.This may be why AI Mode currently adds specific geographic and temporal contextual statements even where not necessarily required – often it appears to be more of a flex than an effort to offer additional value.
- Super-Local Brand Responses: Queries about large brands, such as NASA, sometimes triggered hyperlocal suggestions.
- Occasional Failures and Irrelevant Citations: Users sometimes encountered errors or citations that had no clear connection to the query.
These observations underscore that AI Mode is still evolving, with Google continuously refining how it retrieves, ranks, and presents content.
What does the AI Mode interface look like?
Several more current examples of the AI Mode UI have surfaced since we initially covered its appearance in testing. We’ve kept our earlier coverage here for reference purposes.
To see the latest examples of the AI Mode UI, see immediately below. For the outdated coverage — keep scrolling.
Desktop:
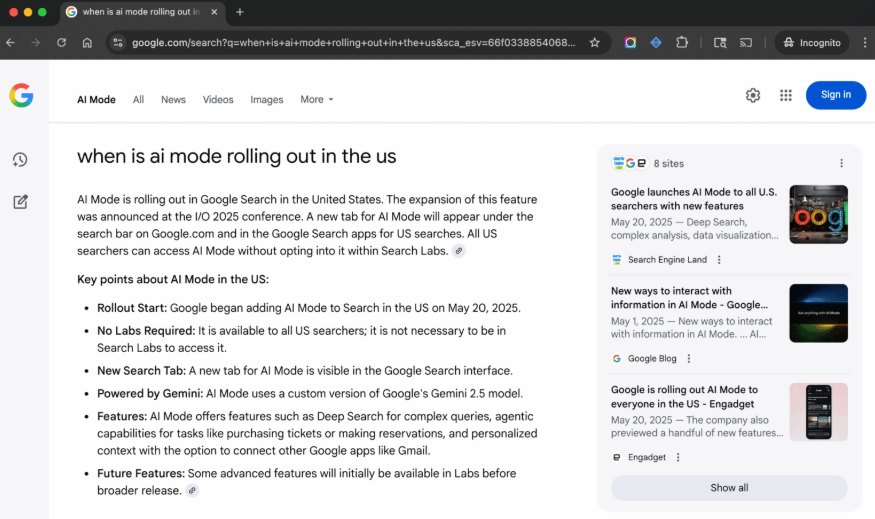
Source: Search Engine Land
Mobile:
Here's the top portion of an AI Mode results page on mobile.
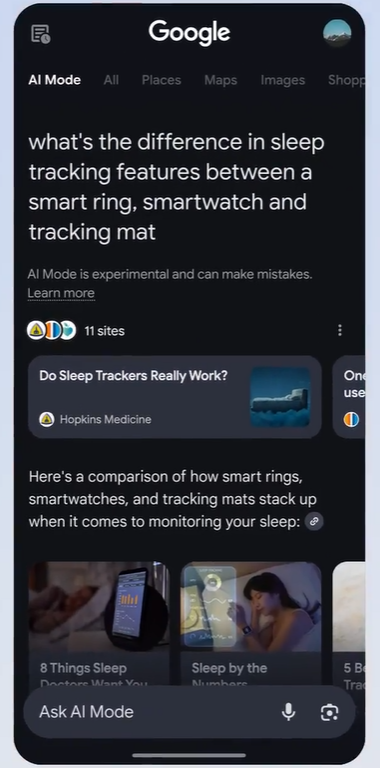
Source: Google
And here's a bit further down the page for that same AI Mode search.
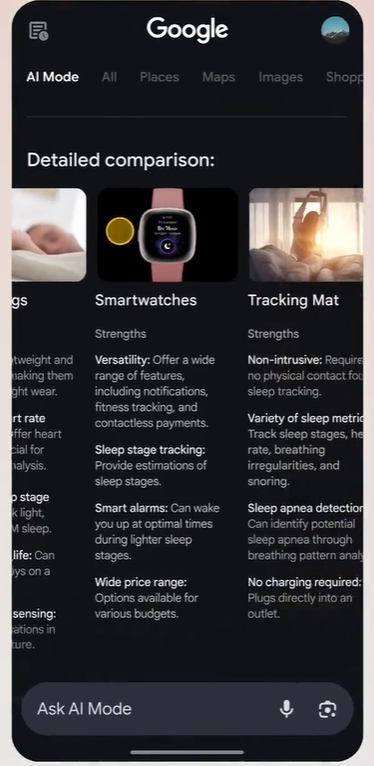
What does Google AI Mode look like? (Outdated coverage)
Below is a screenshot of the AI Mode UI for desktop; it is the only UI image available at this time.
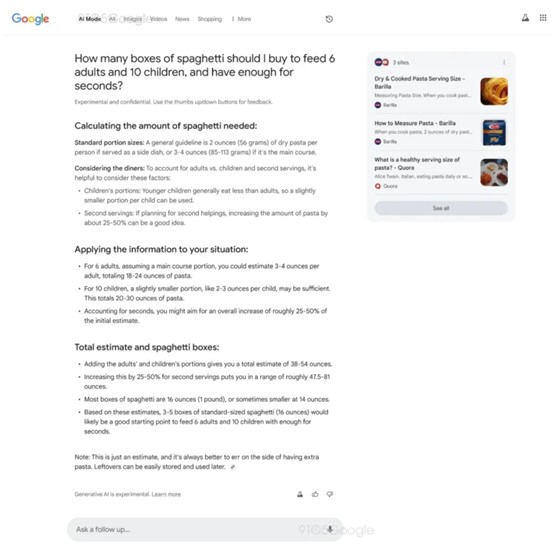
Source: Searchengineland
Based on this screenshot, it appears that users type queries in the normal search bar and then activate AI Mode using a new filter that appears next to the usual options, i.e., ‘Images’, ‘Shopping’, ‘News’, etc.
By keeping the standard search interface intact while offering AI Mode as an optional feature, Google could limit the inevitable negative impact on web traffic, ensuring that users continue to interact with organic search results. This would also help protect the viability of traditional Search Ads and Display Ads. As we mentioned in our guide to SGE, if these ads stopped generating traffic, Google would lose a significant portion of their revenue.
AI Mode itself looks like a large AI Overview sans traditional SERPs — instead offering a card to the right that contains links to explore the web.
As you can see at the bottom of the screenshot, there’s a field available to ask follow-up questions.
Although no mobile device UI screenshots have surfaced yet, Android Authority managed to activate the mobile UI that contains the AI Mode button. The button in question features a magnifying glass icon with a rainbow border on the top left-hand side of the UI pictured below:
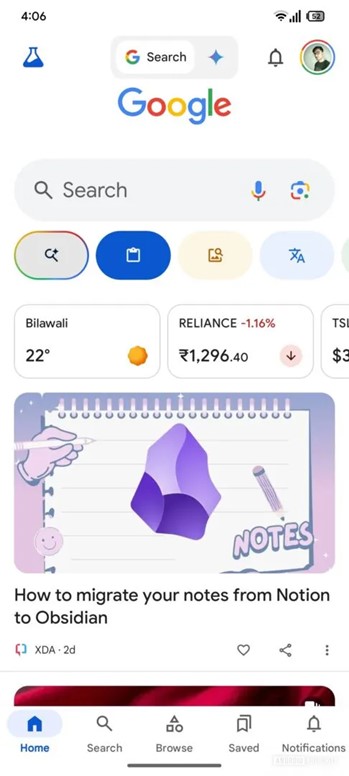
Source: Androidauthority
It didn’t work when tapped, as the feature is still in development, but it’s interesting to see how access looks — at least at this early stage.
The Android Authority team also spotted a button for AI Mode in the ‘Shortcuts’ menu in the Google Search widget:
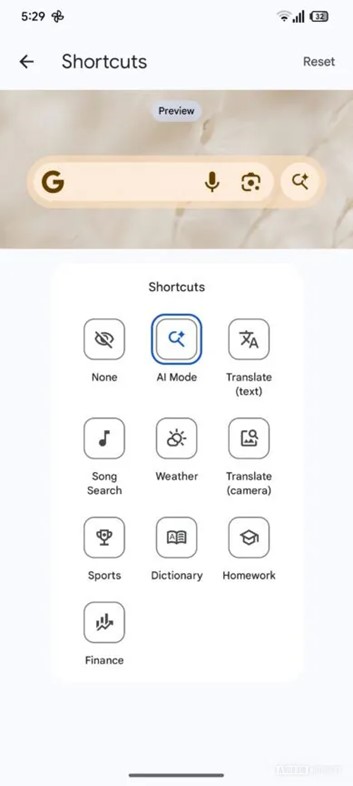
Will there be ads in AI Mode?
Google confirmed in March 2025 that they will test ads in AI Mode, drawing on lessons learned from AI Overviews. Ads may appear below generated outputs or potentially be integrated more creatively (e.g., native placements within conversational responses).
Balancing sponsored content and user trust will be critical for Google.
For advertisers, the context-rich interactions between users and AI Mode paves the way for hyper relevant ad placements, which could potentially drive bigger ROAS.
How can businesses prepare?
Preparing for the public release of Google’s AI Mode should centre on building visibility in AI search responses.
- Strengthen SEO fundamentals, since strong rankings in traditional SERPs increase the chance of being cited.
- Track dynamic retrieval, as the rotation of sources on refresh can surface less-prominent websites.
- Optimise structured data and on-page content to improve citation likelihood and passage-level relevance.
At TDMP, we’re building advanced attribution tracking to help brands see exactly where and how they appear in AI search responses — so our clients can adjust their digital strategy as search behaviours evolve.
Get in touch to see how we can help drive your success as search behaviours shift.
How was AI Mode revealed?
At TDMP, we’ve tracked Google’s integration of AI into Search for years, analysing its implications, predicting developments, and reporting on progress at several key stages:
- Google Bard, ChatGPT, Microsoft Bing: How AI is changing SEO – A deep dive into early AI-driven search shifts.
- Google to introduce generative AI responses in SERPs – Our early coverage of Google’s move toward AI-powered results.
- Preparing for Google SGE – full breakdown – Insights on how Search Generative Experience (SGE) would inform search strategies.
- Google launches AI Overviews: Key features and updates – Tracking Google’s transition from SGE to AI Overviews and its immediate impact.
We’ve been anticipating the arrival of Google Gemini Search for some time, first bringing it to your attention in our May 2024 article ‘What Google’s March update reveals about the future of SEO’.
However, the most concrete evidence of an AI Mode nearing completion came from 9to5Google. They did so by “decompiling” the files (APKs) that make up the latest version of the Google Search app for Android.
This process reveals code that serves as clues as to what Google is working on — and even what features larger projects could have upon release, but bear in mind that nothing is certain.
As 9to5Google explained, ‘Google may… not ever ship these features’, but it’s an intriguing glimpse into the early ideas in consideration.
The code referring to AI Mode (given as ‘aim’ in the code) can be traced back to October 2024 but has continued to appear in more recent iterations of Google’s app.
Reportedly, below are some examples of the code in question:
<string name=”googleapp_aim_mic_button_content_description”>Microphone</string>
<string name=”googleapp_aim_listening_text”>Listening…</string>
<string name=”googleapp_aim_photo_button_content_description”>Take a photo</string>
<string name=”googleapp_aim_gallery_button_content_description”>Add image from gallery</string>
<string name=”googleapp_aim_followup_hint”>Ask a follow up…</string>
<string name=”googleapp_aim_interrupt_button_content_description”>Stop loading</string>
Note that there is a reference to a ‘mic button’ for voice search and ‘photo’/’gallery’ buttons for image-based additions.
There’s also an ‘Ask a follow-up’ option — as is expected of an AI search facility.
A leaked email revealed more
Shortly after 9to5Google’s exploration, a leaked internal Google email asking employees to test AI Mode has shed more light on the project.
In the email, Google describes AI Mode as ‘Search intelligently researching for you — organising information into easy-to-digest breakdowns with links to explore content across the web.’
They also mention that this new search format is designed to handle exploratory questions that are currently ‘not well served’ by typical search results. Here are some query examples given in the email:
- ‘How many boxes of spaghetti should I buy to feed 6 adults and 10 children, and have enough for seconds’
- ‘Compare wool, down, and synthetic jackets in terms of insulation, water resistance, and durability’
- ‘What do I need to get started with aquascaping?’
[Follow-up]: ‘What are some nearby stores to buy supplies?’

